🎄欢迎来到@边境矢梦°的csdn博文🎄
🎄本文主要梳理手动实现Spring底层机制🎄
🌈我是边境矢梦°,一个正在为秋招和算法竞赛做准备的学生🌈
🎆喜欢的朋友可以关注一下🫰🫰🫰,下次更新不迷路🎆
Ps: 月亮越亮说明知识点越重要 (重要性或者难度越大)🌑🌒🌓🌔🌕
目录
实现任务阶段 1- 编写自己 Spring 容器,实现扫描包, 得到 bean 的 class 对象
实现任务阶段 2- 扫描将 bean 信息封装到 BeanDefinition 对象, 并放入到 Map
实现任务阶段 3- 初始化 bean 单例池,并完成 getBean 方法 , createBean 方法
我把下面的代码放到了GitHub托管平台上了, 如果有需要的童鞋可以去取https://github.com/luoxiongbo/code.git

实现任务阶段 1- 编写自己 Spring 容器,实现扫描包, 得到 bean 的 class 对象
1. 先用maven将项目框架搭起来, 大致的包结构

2. 在annotation包下创建ComponentScan 和 Component 注解
import com.lxbStu.spring.annotation.ComponentScan;
@ComponentScan(value = "com.lxbStu.spring.component")
public class LxbSpringConfig {
}@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}3. 在ioc包下创建要给配置配LxbSpringConfig, 充当.xml的作用
@ComponentScan(value = "com.lxbStu.spring.component")
public class LxbSpringConfig {
}4. 在component包下创建bean
@Component("monsterService")
public class MonsterService {
}@Component("monsterDao")
public class MonsterDao {
}5. 在ioc包下创建我们自己写的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
public class LxbSpringApplicationContext {
private Class config;
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singleton = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> getIoc() {
return singleton;
}
public Object getBean(String bean) {
return singleton.get(bean);
}
public LxbSpringApplicationContext(Class ClassConfig) {
this.config = ClassConfig;
ComponentScan component = (ComponentScan) config.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = component.value();
path = path.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println("扫描的路径是 : " + path);
System.out.println("=====================================================");
ClassLoader classLoader = LxbSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
//System.out.println(resource);
File ComponentFile = new File(resource.getFile());
if(ComponentFile.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = ComponentFile.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
String classPath = file.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("类的绝对路径是 : " + classPath);
if(classPath.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = classPath.substring(classPath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, classPath.indexOf(".class"));
String classFullPath = path.replace("/", ".") + "." + className;
System.out.println("类的全路径是 :" + classFullPath + ", 类名是 :" + className);
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classFullPath);
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component beanId = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String value = beanId.value();
if(value == null || "".equals(value)) {
value = className.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + className.substring(1);
}
//System.out.println(value);
System.out.println("是一个 bean = " + clazz);
try {
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
singleton.put(value, instance);
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
System.out.println("不是一个 bean = " + clazz);
}
System.out.println("=====================================================");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
}6. 测试
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void ConfigTest() {
LxbSpringApplicationContext ioc = new LxbSpringApplicationContext(LxbSpringConfig.class);
//ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> beans = ioc.getIoc();
//Enumeration<String> keys = beans.keys();
//while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
// String id = keys.nextElement();
// System.out.println(beans.get(id));
//}
}
}结果 :
扫描的路径是 : com/lxbStu/spring/component
=====================================================
类的绝对路径是 : D:\code\java\lxb-spring\target\classes\com\lxbStu\spring\component\Car.class
类的全路径是 :com.lxbStu.spring.component.Car, 类名是 :Car
是一个 bean = class com.lxbStu.spring.component.Car
=====================================================
类的绝对路径是 : D:\code\java\lxb-spring\target\classes\com\lxbStu\spring\component\MonsterDao.class
类的全路径是 :com.lxbStu.spring.component.MonsterDao, 类名是 :MonsterDao
是一个 bean = class com.lxbStu.spring.component.MonsterDao
=====================================================
类的绝对路径是 : D:\code\java\lxb-spring\target\classes\com\lxbStu\spring\component\MonsterService.class
类的全路径是 :com.lxbStu.spring.component.MonsterService, 类名是 :MonsterService
是一个 bean = class com.lxbStu.spring.component.MonsterService
=====================================================
实现任务阶段 2- 扫描将 bean 信息封装到 BeanDefinition 对象, 并放入到 Map
1. 在annotation中创建Scope, 用来注解类是单例还是多例
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Scope {
String value();
}2. 修改component包中的MonsterService
@Component("monsterService")
@Scope("prototype")
public class MonsterService{}3. 在ioc中创建BeanDefinition, 用于存放bean的元数据, bean类的数据
public class BeanDefinition {
private Class clazz;
private String scope;
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
public Class getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BeanDefinition{" +
"clazz=" + clazz +
", scope=" + scope +
'}';
}
}4. 重新写LxbSpringApplicationContext, 将bean的定义放到beanDefinitionMap中
public class LxbSpringApplicationContext {
// 配置类
private Class config;
// 存放单例bean的map
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singleton = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 存放bean元数据的map
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 返回单例map
public ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> getIoc() {
return singleton;
}
// 返回bean根据 id
public Object getBean(String bean) {
return singleton.get(bean);
}
// 将从包中扫描类的步骤封装起来, 封装到这个方法中
public void LoaderResourceByConfig(Class ClassConfig) {
this.config = ClassConfig;
ComponentScan component = (ComponentScan) config.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = component.value();
path = path.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println("扫描的路径是 : " + path);
System.out.println("=====================================================");
ClassLoader classLoader = LxbSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
//System.out.println(resource);
File ComponentFile = new File(resource.getFile());
if (ComponentFile.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = ComponentFile.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
String classPath = file.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("类的绝对路径是 : " + classPath);
if (classPath.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = classPath.substring(classPath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, classPath.indexOf(".class"));
String classFullPath = path.replace("/", ".") + "." + className;
System.out.println("类的全路径是 :" + classFullPath + ", 类名是 :" + className);
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classFullPath);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component beanId = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String id = beanId.value();
if (id == null || "".equals(id)) {
id = className.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + className.substring(1);
}
//System.out.println(value);
System.out.println("是一个 bean = " + clazz);
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
Scope scope = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());
} else {
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(id, beanDefinition);
} else {
System.out.println("不是一个 bean = " + clazz);
}
System.out.println("=====================================================");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
// 构造器, 参数是配置类
public LxbSpringApplicationContext(Class ClassConfig) {
LoaderResourceByConfig(ClassConfig);
}
}结果 :

实现任务阶段 3- 初始化 bean 单例池,并完成 getBean 方法 , createBean 方法
1. 将bean根据单例还是多例进行实例化, 将单例进行实例化放到singletonMap中, 多例不进行实例化
// 返回bean根据 id
public Object getBean(String bean) {
if(beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(bean)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(bean);
if(beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")) {
return singletonMap.get(bean);
} else {
return create(bean);
}
} else {
throw new NullPointExecption("不存在的bean");
}
}
public Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
try {
return clazz.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}2. 测试类Test
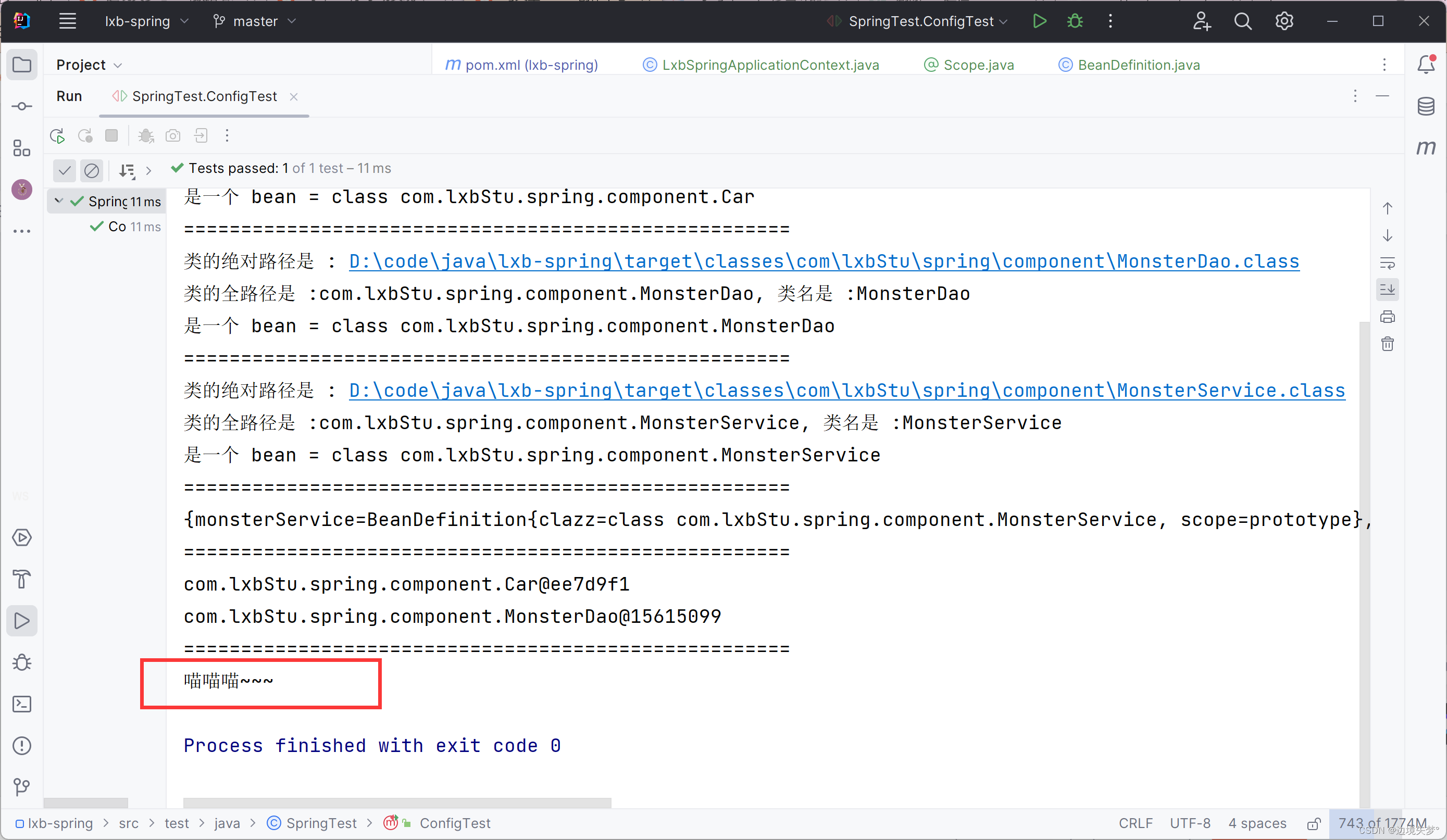
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void ConfigTest() {
LxbSpringApplicationContext ioc = new LxbSpringApplicationContext(LxbSpringConfig.class);
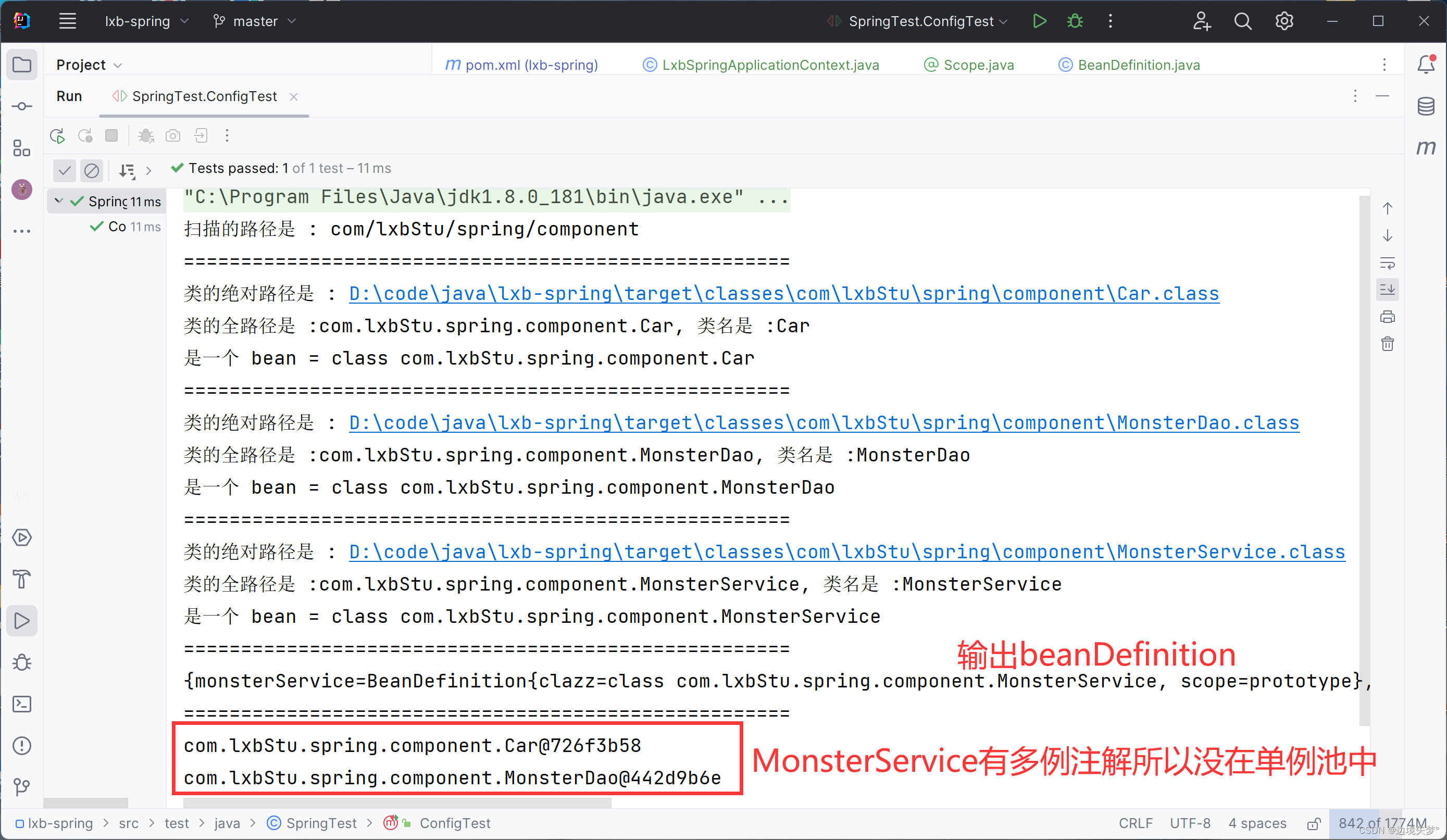
System.out.println("=====================================================");
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> beans = ioc.getIoc();
Enumeration<String> keys = beans.keys();
while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
String id = keys.nextElement();
System.out.println(beans.get(id));
}
}
}结果 :
实现任务阶段 4- 完成依赖注入
1. 在annotation中创建注解Autowired
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD})
public @interface Autowired {
//一个属性 required ,这里我们就不讲了,也比较简单, 有兴趣同学们作为课后加入
//String required() default "true";
}2. 修改component中的MonsterService和MonsterDao
@Component("monsterDao")
public class MonsterDao {
public void hi() {
System.out.println("喵喵喵~~~");
}
}@Scope("prototype")
@Component("monsterService")
public class MonsterService {
@Autowired
private MonsterDao monsterDao;
public void m1() {
monsterDao.hi();
}
}3. 修改LxbSpringApplicationContext, 中的createBean方法, 在实例化对象的时候将域中需要注入的属性进行注入
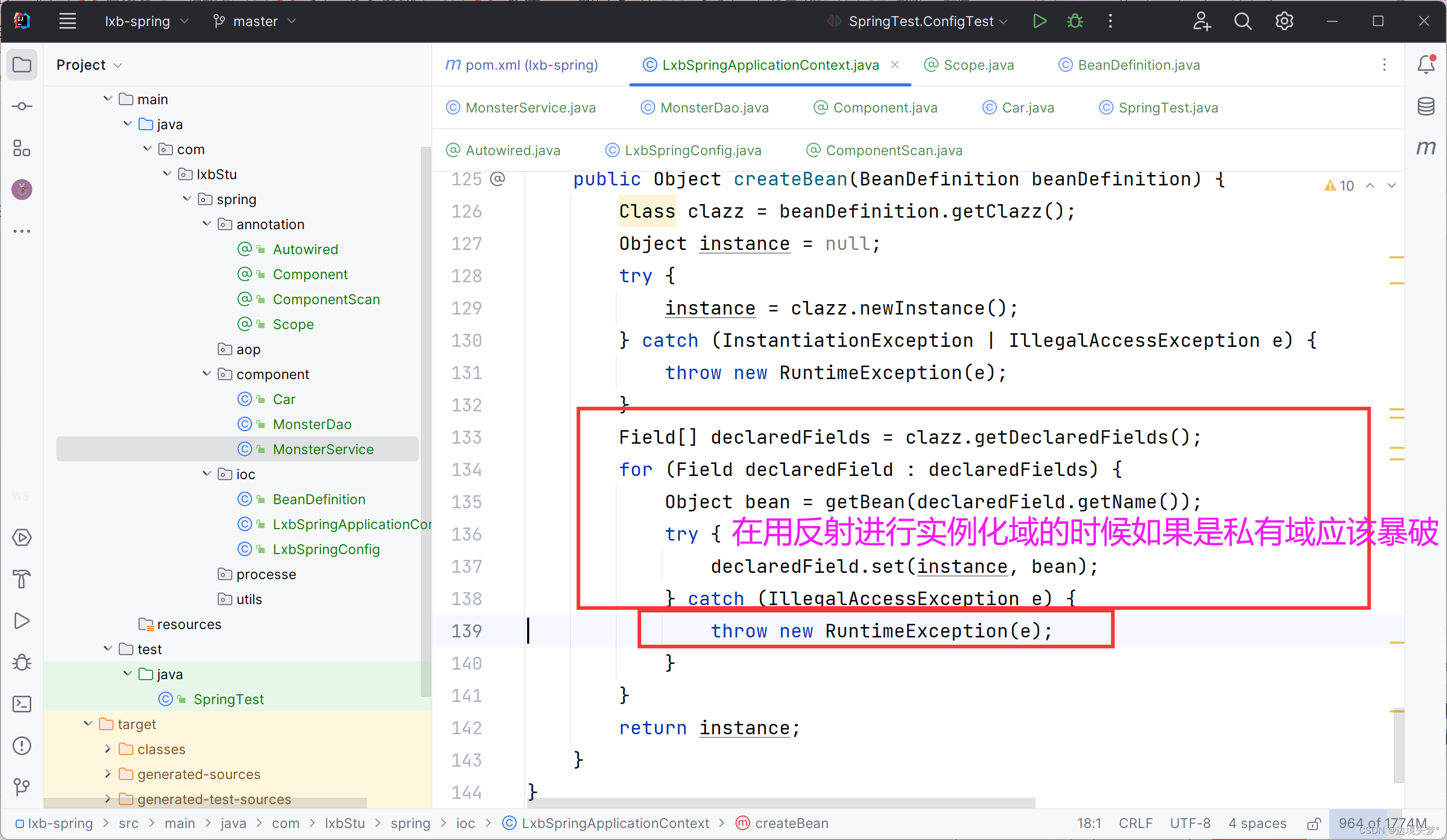
public Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
Object instance = null;
try {
instance = clazz.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
Object bean = getBean(declaredField.getName());
try {
declaredField.set(instance, bean);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return instance;
}结果 :

原因分析 :
修改如下图 :
结果 :
实现任务阶段 5- bean 后置处理器实现
1. 对于初始化方法, 我们写一个接口InitializingBean, 如果一个类实现了就说明bean含有初始化方法, 反之, 亦然.
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
2. 修改 MonsterDao 类, 实现接口 InitializingBean , 实现它的方法, 让该类有初始化方法
@Component("monsterDao")
public class MonsterDao implements InitializingBean {
public void hi() {
System.out.println("喵喵喵~~~");
}
/**
* 就像之前那样, 我们是通过写一个方法在xml中配置属性的时候给初始化的属性进行赋值
* 初始化方法可有可无, 但是后置处理器是
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("MonsterService 进行初始化, 具体业务由程序员来搞定....");
}
}3. 先用简单的步骤测试实现方法的类在create的时候会不会执行初始化方法
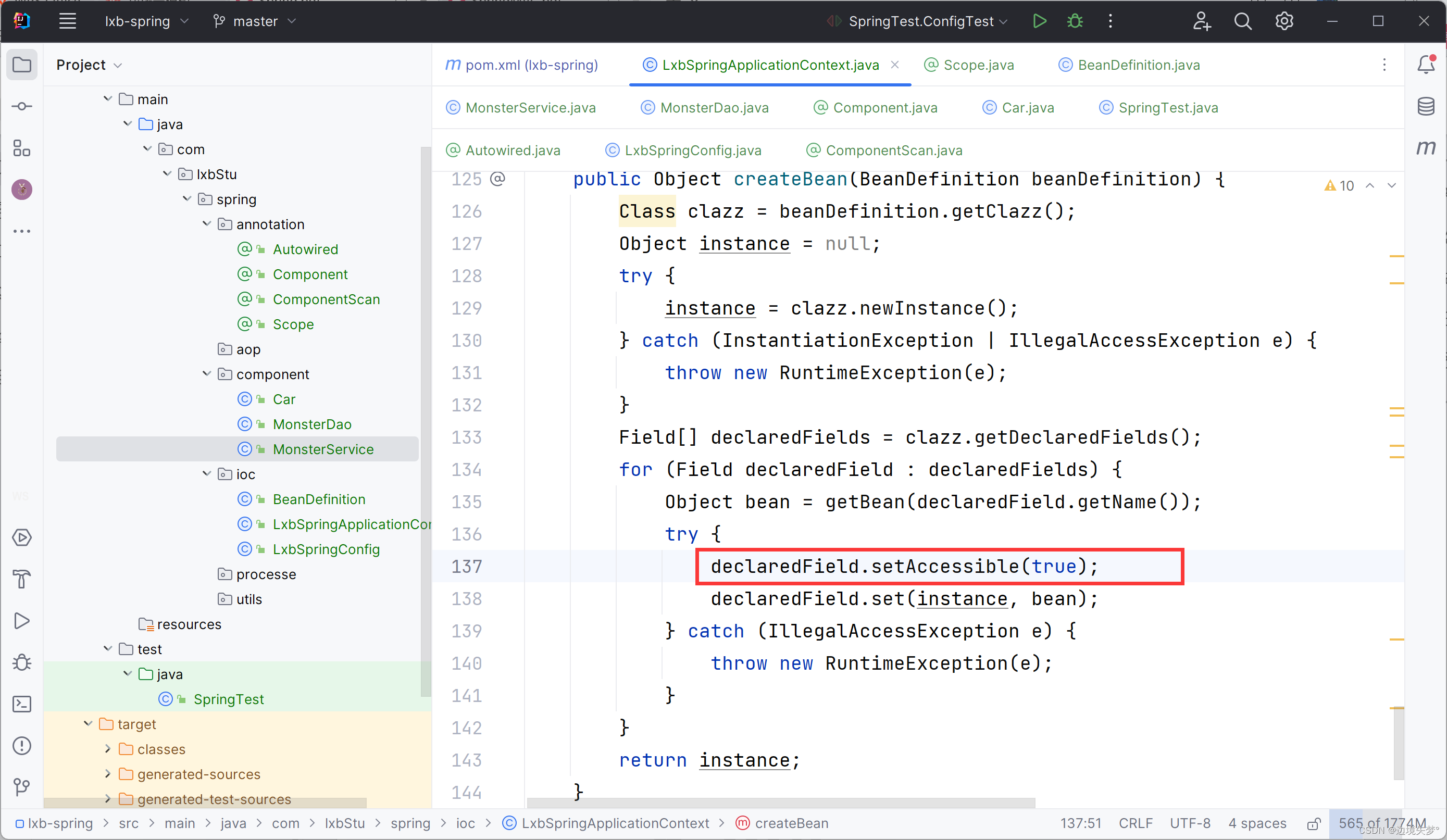
public Object createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
Object instance = null;
try {
instance = clazz.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
Object bean = getBean(declaredField.getName());
try {
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(instance, bean);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("=====================创建好了实例======================");
if(instance instanceof InitializingBean) {
try {
((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertiesSet();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return instance;
}结果 :

4. 后置处理器接口的实现, 在processe中进行创建
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
//bean 初始化前执行的业务
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName);
//bean 初始化后执行的业务
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName);
}5. 在component中创建LxbBeanPostProcessor, 用来进行后置处理
@Component
public class LxbBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization 被调用 " + beanName + " bean= " + bean.getClass());
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization 被调用 " + beanName + " bean= " + bean.getClass());
return bean;
}
}6. 修改ioc的SpringApplicationContext中的扫描方法和createBean() 方法, 在扫描的时候将他们进行实例化并放到beanPostProcessorMap中, 在create的时候调用所有的后置处理器
扫描方法
public void LoaderResourceByConfig(Class ClassConfig) throws RuntimeException {
this.config = ClassConfig;
ComponentScan component = (ComponentScan) config.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = component.value();
path = path.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println("扫描的路径是 : " + path);
System.out.println("=====================================================");
ClassLoader classLoader = LxbSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
//System.out.println(resource);
File ComponentFile = new File(resource.getFile());
if (ComponentFile.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = ComponentFile.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
String classPath = file.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("类的绝对路径是 : " + classPath);
if (classPath.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = classPath.substring(classPath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, classPath.indexOf(".class"));
String classFullPath = path.replace("/", ".") + "." + className;
System.out.println("类的全路径是 :" + classFullPath + ", 类名是 :" + className);
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classFullPath);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component beanId = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String id = beanId.value();
if (id == null || "".equals(id)) {
id = className.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + className.substring(1);
}
//System.out.println(value);
System.out.println("是一个 bean = " + clazz);
if(clazz.isAssignableFrom(BeanPostProcessor.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor) clazz.newInstance();
beanPostProcessorList.add(beanPostProcessor);
continue;
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
Scope scope = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());
} else {
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(id, beanDefinition);
} else {
System.out.println("不是一个 bean = " + clazz);
}
System.out.println("=====================================================");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}createBean()方法
public Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
Object instance = null;
try {
instance = clazz.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
Object bean = getBean(declaredField.getName());
try {
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(instance, bean);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("===============创建好了实例 Set 方法执行完===============");
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
Object temp = beanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(instance, beanName);
if(temp != null) {
instance = temp;
}
}
if(instance instanceof InitializingBean) {
try {
((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertiesSet();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
for(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
Object temp = beanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(instance, beanName);
if(temp != null) {
instance = temp;
}
}
return instance;
}结果 :
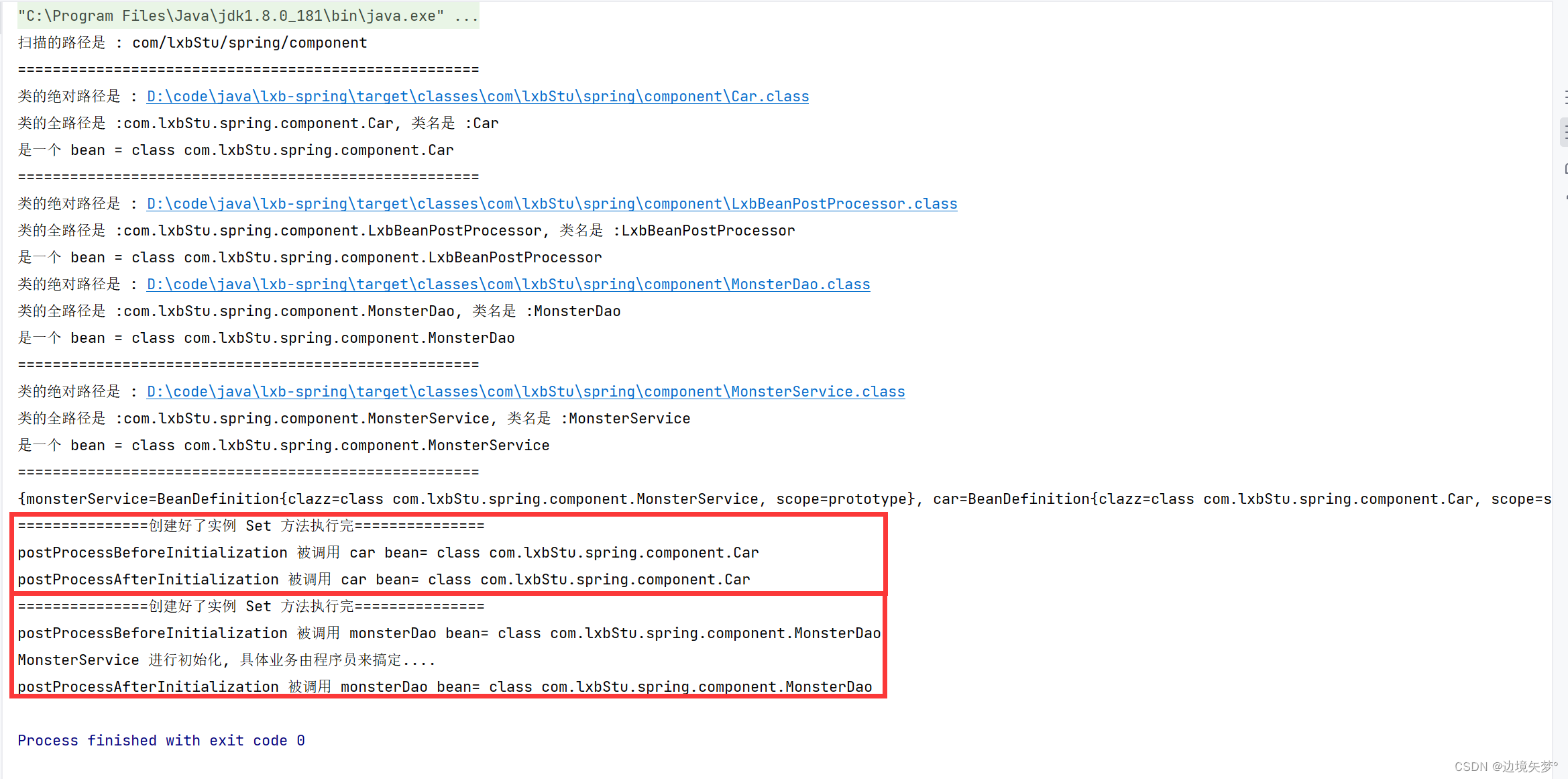
实现任务阶段 6- AOP 机制实现
1. 在component中创建SmartAnimalable, 以它为接口, 我们写类去实现它, 用动态代理实现切面编程
public interface SmartAnimalable {
float getSum(float i, float j);
float getSub(float i, float j);
}2. 在component中创建SmartDog类去实现SmartAnimalable
@Component("smartDog")
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimalable{
@Override
public float getSum(float i, float j) {
float result = i + j;
System.out.println("getSum() 方法内部打印 result= " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public float getSub(float i, float j) {
float result = i - j;
System.out.println("getSub() 方法内部打印 result= " + result);
return result;
}
}3. 在annotation中创建注解Aspect, After, Before
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface After {
String value();
}@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Before {
String value();
}@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Aspect {
String value() default "";
}4. 在component中创建SmartAnimalAspect该类就是切面类, 对注解了的类的方法进行切面
@Aspect
@Component
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
@Before("execution com.lxbStu.spring.component.SmartDog getSum")
public void showBeginLog() {
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@After("execution com.lxbStu.spring.component.SmartDog getSum")
public void showSuccessEndLog() {
System.out.println("返回通知");
}
}5. 在aop中创建一个工具类, 用于存放aspect对应那个类的那个方法的关系, 为了简化操作将该类的属性和方法设置为静态
public class AspectContainer {
private static final ConcurrentHashMap<Class, String[]> aspectJMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public static void add(Class clazz, String[] value) {
aspectJMap.put(clazz, value);
}
public static ConcurrentHashMap<Class, String[]> getAspectJ() {
return aspectJMap;
}
}6. 修改LxbSpringApplicationContext类中的LoaderResourceByConfig()方法在扫描的时候将切面类的信息封装到AspectContainer中的Map里面, 为了方便之后后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法之后执行时直接查找是否某个类可以用到切面类
public void LoaderResourceByConfig(Class ClassConfig) throws RuntimeException {
this.config = ClassConfig;
ComponentScan component = (ComponentScan) config.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
String path = component.value();
path = path.replace(".", "/");
System.out.println("扫描的路径是 : " + path);
ClassLoader classLoader = LxbSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
//System.out.println(resource);
File ComponentFile = new File(resource.getFile());
if (ComponentFile.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = ComponentFile.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println("=====================================================");
String classPath = file.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("类的绝对路径是 : " + classPath);
if (classPath.endsWith(".class")) {
String className = classPath.substring(classPath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, classPath.indexOf(".class"));
String classFullPath = path.replace("/", ".") + "." + className;
System.out.println("类的全路径是 :" + classFullPath + ", 类名是 :" + className);
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classFullPath);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component beanId = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
String id = beanId.value();
if (id == null || "".equals(id)) {
id = className.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase() + className.substring(1);
}
//System.out.println(value);
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Aspect.class)) {
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
String classAndMethod = null;
if(method.getDeclaredAnnotation(Before.class) != null) {
Before before = method.getDeclaredAnnotation(Before.class);
classAndMethod = before.value();
}
if(method.getDeclaredAnnotation(After.class) != null) {
After after = method.getDeclaredAnnotation(After.class);
classAndMethod = after.value();
}
if(classAndMethod != null) {
// 我只需要把aspect方法里的注解的信息进行分析就可以了, 至于aspect只需要将它的对象的路径放在字符串数组中即可
String[] split = classAndMethod.split(" ");
Class<?> key = Class.forName(split[1]);
String methodName = split[2];
String[] value = new String[] {methodName, classFullPath};
// 封装为 = 类路径 + 方法
AspectContainer.add(key, value);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("是一个 AspectJ = " + clazz);
continue;
}
// 这行很重要
if(BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor = (BeanPostProcessor) clazz.newInstance();
beanPostProcessorList.add(beanPostProcessor);
System.out.println("是一个 BeanPostProcessor = " + clazz);
continue;
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
Scope scope = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(scope.value());
} else {
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
beanDefinitionMap.put(id, beanDefinition);
System.out.println("是一个 bean = " + clazz);
} else {
System.out.println("不是一个 bean = " + clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}7. 修改component中的LxbBeanPostProcessor类后置处理器中的postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法, 保证在后置处理器的after方法中返回代理对象, 并将执行逻辑进行修改
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization 被调用 " + beanName + " bean= " + bean.getClass());
ConcurrentHashMap<Class, String[]> aspectJ = AspectContainer.getAspectJ();
String[] strings = aspectJ.get(bean.getClass());
if(strings != null) {
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(LxbBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
if (strings[0].equals(method.getName())) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(strings[1]);
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
Method before = SpringUtils.FindMethodByName(methods, "showBeginLog");
before.invoke(clazz.newInstance());
result = method.invoke(bean, args);
Method after = SpringUtils.FindMethodByName(methods, "showSuccessEndLog");
after.invoke(clazz.newInstance());
} else {
result = method.invoke(proxy, args);
}
return result;
}
});
return proxyInstance;
}
return bean;
}8. 测试类
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void ConfigTest() {
LxbSpringApplicationContext ioc = new LxbSpringApplicationContext(LxbSpringConfig.class);
System.out.println("=====================================================");
//ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> beans = ioc.getIoc();
//Enumeration<String> keys = beans.keys();
//while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
// String id = keys.nextElement();
// System.out.println(beans.get(id));
//}
//MonsterService monsterService = (MonsterService) ioc.getBean("monsterService");
//monsterService.m1();
//ConcurrentHashMap<Class, String[]> aspectJ = AspectContainer.getAspectJ();
//Enumeration<Class> keys = aspectJ.keys();
//while(keys.hasMoreElements()) {
// Class aClass = keys.nextElement();
// String[] strings = aspectJ.get(aClass);
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));
//}
SmartAnimalable bean = (SmartAnimalable) ioc.getBean("smartDog");
float sum = bean.getSum(1, 9);
}
}结果 :

最后项目的结是 :








